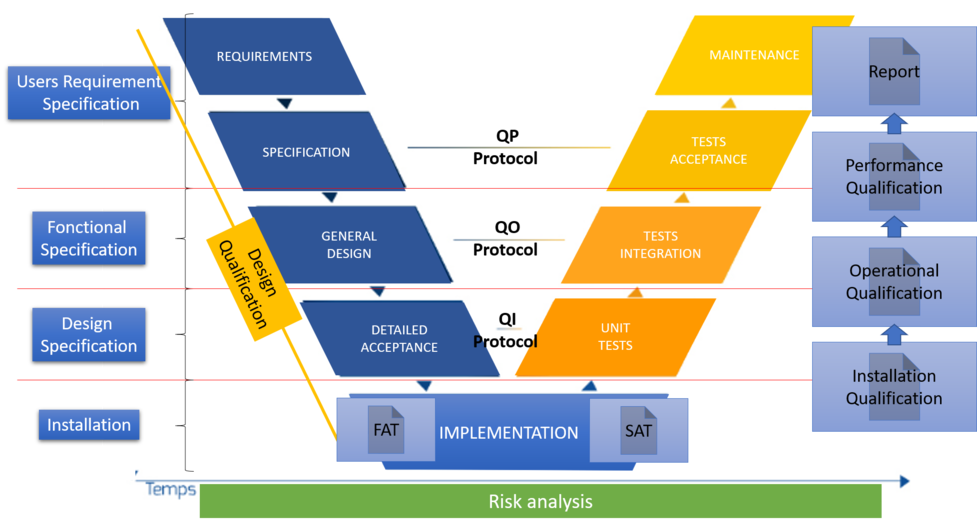
In the phases, we have:
- Requirements that are defined by the following:
- USRs or user specifications or business specifications,
- SPs or functional specifications,
- DS or design specifications,
- Design qualification (DQ).
- The choice of the solution.
- The FAT or Factory Acceptance Test (test performed by the supplier on his site, which makes it possible to verify the correct answer to the requirements of the solution),
- SAT or Site Acceptance Test (Test performed by the supplier on the site, which makes it possible to verify that the solution always meets the requirements once installed in a client environment).
- Implementation, installation of the solution
- An IQ or installation qualification is performed to ensure that the elements are properly installed in the right place and that the information provided by the supplier is correct. This phase makes it possible to trace the elements, version, part, serial number ... It is a question of checking the adequacy with the DS.
- The OQ or operational qualification
- It makes it possible to verify that the operation of the solution responds to the expected through the implementation of tests and documented evidence. This is to check the agreement with the FS.
- QP or performance qualification
- It makes it possible to check the proper functioning of the process put in place to guarantee the correct operation in routine, the operation must be reproducible 3 times (or more / less: function of the Risk Assessment) to validate the good functioning of the process.
- Authorization for routine use of the solution
- After validation of all the elements a routine authorization of use and a report are then written with all the elements. This step definitely consolidates the response to the URS.
An authorization with a formalized review is made at each step to ensure validation and optimum quality.
The realization of the tests and the effort to put in place is seen via an AR (Risk Analysis) based on the regulations in force and the user specifications (USR), among others, the business risks, the risks for the health of the patients , the system architecture and its components, CQA (Critical Quality Attributes) and CPP (Critical Process Parameters).
Key generic roles (may vary by laboratory)
- Process owner, expresses the need, approves the solution if it complies with the expectation,
- Engineering, formalizes the need for technical response, runs test protocols, installs the solution with the vendor, formalizes the change request,
- Validation and Quality ensure that the solution meets regulatory requirements and does not pose a risk to patient safety. This entity, drafts, risk analysis, test protocols, supervises their executions, verifies the evidence and documentation, validates the request for change,
- The vendor provides the solution and associated documentation, trains users, and installs the solution with engineering.
Tips and tricks
- Respect the steps for a successful project on time.
- Have the expression of the need as soon as possible in order to immediately identify the effort to implement the solution.
- The VMP (validation plan or Validation master plan) must be up to date with the qualification process that must be implemented. Ideally, we must find the validation matrix that takes the needs and constraints.
- Integrate the regulations in force with the functionality of the solution when writing the risk analysis.
- The writing and use of generic qualification protocol require a greater effort at the beginning on the editorial part of the protocols but the time saving will become even more important once set up.
Reminder: All changes must be subjected to a change request even solution updates. During an update, if the design is not modified, it is not necessary to redo its qualification provided that this possibility is indicated in the validation process management documents (VMP for example).
In conclusion
The V cycle in its pharmaceutical form allows a sequencing of steps to cover the different stages of validation in terms of traceability on a 4Q model (CQ, IQ, OQ, PQ), with the notion of protocol, tests, and report. This allows us to have the writing of what we should do, do what we wrote, and write what we did.