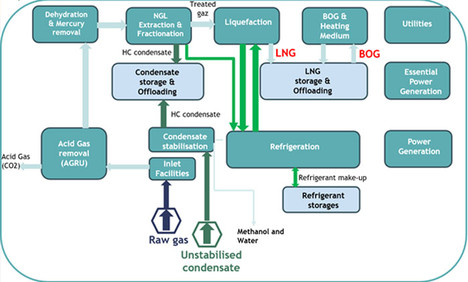
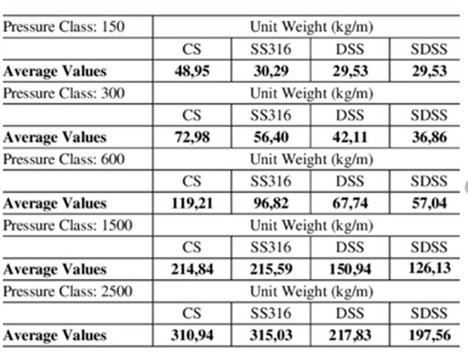
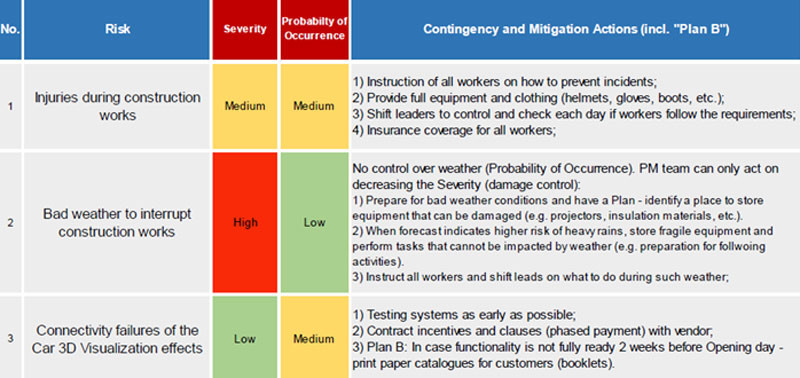
Project Management skills
On top of technical skills, the PM needs to master the regular skills of project management on planning, scheduling, human resources…
Planning
The Project Manager shall consider several parameters to create a realistic planning. This planning is based on a practical time schedule and an optimized budget. The planning is considering the parameters below:
- The chosen technology. If it is a GBS (Gravity Based Structure) for example, the planning shall consider a towing phase that can occur only in the Summer if the plant in is the Arctic for example. In this case, after October the towing will not be possible because of the ice and the project will automatically be delayed one year.
- The mobilization of the teams. The PM shall identify all the skills required during the project and assign a duration for each task to mobilize people as per a clear mobilization plan.
- The execution of the project. The fabrication of the station will consist of a thousand tasks. The excavation, the procurement, the rebars installation, the inspections for quality, the pouring of concrete, the welding of kilometers of piping, the pressure tests of the piping systems shall be scheduled to avoid clash on site and to optimize the activities on site. The sequence of all the activities shall be correct and considering the characteristics of each task.
Human Management
Usually oil & gas projects can gather thousands of people in the offices and on site. Engineers, supervisors and workers are often expatriated. All these people need accommodation, food, water, etc.
The Project Manager will in a first step identify the different expertise required considering the technology chosen and activities needed to achieve the project (welders, carpenters, engineers, supervisors, etc). Then the number of people for each skill is defined. The human resources department has to hire all these people and manage their mobilization (contracts, flight tickets, accommodation, salary, etc).
On site, in order to reduce the time and cost of the execution, workers are housed near the site. A camp for the workers is usually placed with all amenities (bedrooms, bathrooms, canteen, gym equipment, etc) nearby. The camp reduces the time for the workers to reach the site every morning. In Oil & Gas, the sites are often very far from cities.
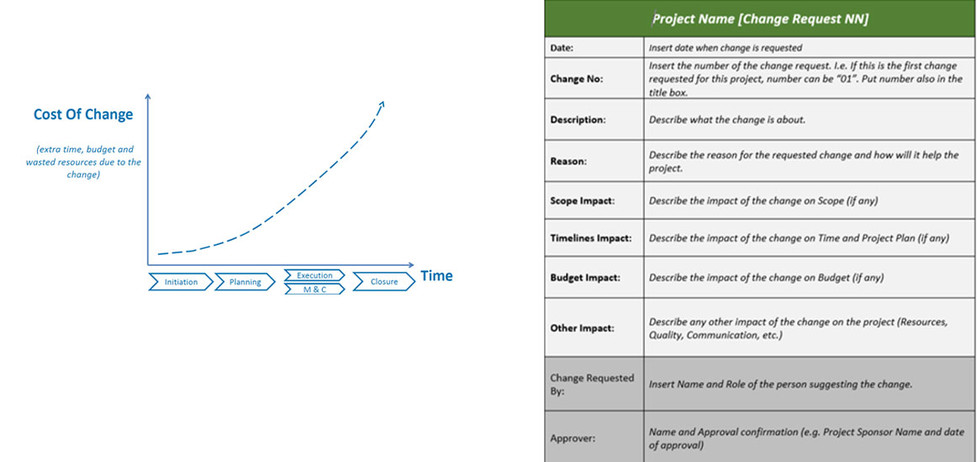
Change Management
In the Oil & Gas industry, the client might require changes to be made during the project lifecycle. Change management is the key to control the cost of the project.
The Project Manager shall put in place a process to analyze the changes required by the client or other stakeholders and estimate the time and cost impact and inform the client. On the right an example of the Change request form.